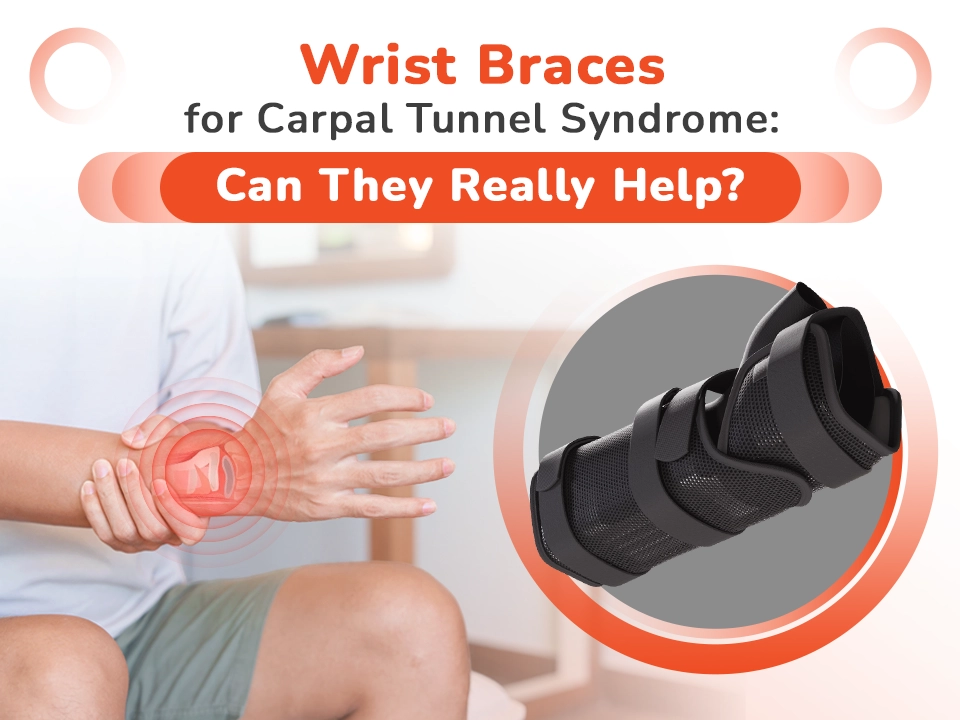
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a prevalent condition affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the narrow carpal tunnel in the wrist, becomes compressed, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. These symptoms can interfere with daily tasks, from typing to holding objects, making CTS not only physically debilitating but also a source of frustration for those affected.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve. However, for many individuals, wrist braces offer a non-invasive, cost-effective, and practical solution to manage symptoms. By providing support and maintaining the wrist in a neutral position, these braces help alleviate discomfort and prevent further nerve irritation.
This article delves into the role of wrist braces in managing CTS, highlighting their benefits, the various types available, and how to choose the right one for your needs. Whether you’re seeking relief from mild discomfort or managing chronic symptoms, understanding how wrist braces work can be a game-changer in your journey toward better wrist health.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve, which travels from the forearm into the palm through the narrow carpal tunnel in the wrist, becomes compressed. This nerve plays a crucial role in hand functionality by controlling sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger and movement in small muscles responsible for fine motor skills. When compressed, the nerve’s functionality is disrupted, leading to discomfort, weakness, and even loss of coordination in severe cases. This condition can make simple tasks challenging and painful, such as typing, writing, or gripping objects.
Common Causes of CTS
CTS can develop due to various factors that increase pressure on the median nerve or alter the structure of the carpal tunnel:
- Repetitive Movements: Frequent hand and wrist motions, such as typing, using a computer mouse, or working on an assembly line, can strain the wrist and lead to inflammation, a common precursor to nerve compression.
- Wrist Anatomy: Some individuals naturally have a smaller carpal tunnel, making them more prone to nerve compression. Swelling or tissue thickening from injury can further narrow the tunnel, exacerbating the problem.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic health issues like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and hypothyroidism can cause nerve damage or increase swelling in the wrist, heightening the risk of CTS.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy often lead to fluid retention and swelling, which can temporarily compress the median nerve and trigger CTS symptoms. Fortunately, this condition usually resolves after childbirth.
- Injuries: Fractures, sprains, or other wrist injuries can disrupt the delicate balance of structures within the carpal tunnel, leading to increased nerve pressure and the onset of CTS symptoms.
Understanding these underlying causes is essential for managing CTS effectively. By addressing risk factors and incorporating preventative measures, such as using ergonomic tools and taking breaks during repetitive tasks, individuals can reduce their chances of developing this condition.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) presents a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity, often interfering with daily tasks and overall quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effectively managing and preventing worsening conditions.
- Numbness or Tingling: This sensation primarily affects the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring fingers, often described as a “pins and needles” feeling. It may start intermittently but become persistent over time, disrupting activities like typing or writing.
- Pain in the Wrist and Hand: Discomfort often starts at the wrist but can radiate up the arm, particularly during repetitive movements. This pain tends to worsen after prolonged use of the hand or during periods of rest, such as nighttime.
- Weakness: Many individuals with CTS report a noticeable decrease in grip strength, making it difficult to hold objects, open jars, or perform fine motor tasks. This weakness stems from reduced functionality in the muscles controlled by the median nerve.
- Burning Sensation: A persistent burning feeling in the affected fingers or palm can make even light touches uncomfortable. This symptom is especially common during flare-ups or after extended hand use.
- Worsening Symptoms at Night: CTS symptoms frequently intensify during sleep due to involuntary wrist positioning. Many individuals wake up with numbness, tingling, or pain, often needing to shake their hands to regain sensation.
Understanding these symptoms helps diagnose CTS early, ensuring timely intervention to prevent further nerve damage and improve overall hand function.
Role of Wrist Braces in Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Wrist braces are one of the most effective non-invasive tools for managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. They are designed to maintain the wrist in a neutral position, reducing strain on the median nerve and relieving discomfort.

Here’s How Wrist Braces Work
- Neutral Positioning: Braces relieve pressure on the median nerve by keeping the wrist straight, addressing the root cause of many CTS symptoms. This neutral alignment is particularly beneficial during tasks requiring repetitive wrist movements or sleeping.
- Immobilization: Wrist braces limit unnecessary movement, reducing strain on the tendons and muscles surrounding the carpal tunnel. This controlled restriction prevents further nerve irritation, allowing it to heal over time.
- Ease of Use: Wrist braces are simple to wear and do not require medical expertise, making them a convenient option for all age groups. They can be easily integrated into daily routines without significant disruption.
- Preventative Use: For individuals at risk of developing CTS—such as those with repetitive hand tasks or underlying health conditions—braces can be a preventative measure by maintaining proper wrist alignment and reducing strain.
- Sleep Support: Nighttime splints are particularly effective in preventing involuntary wrist bending that often exacerbates CTS symptoms during sleep. By maintaining a neutral position, these braces provide relief and ensure better rest.
Wrist braces offer symptomatic relief and support long-term recovery when combined with other interventions like physical therapy or ergonomic adjustments. Their versatility and accessibility make them an indispensable tool in managing CTS.
Benefits of Using Wrist Braces for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Wrist braces offer a wide range of benefits for managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) symptoms, making them a cornerstone of non-invasive treatment plans. These devices provide relief and support while empowering individuals to continue their daily activities with reduced discomfort.

- Symptom Relief: Braces help alleviate pain, numbness, and tingling by maintaining the wrist in a neutral position. This alignment minimizes pressure on the median nerve, addressing the root cause of many CTS symptoms and providing immediate relief.
- Non-Invasive Solution: Unlike surgical procedures, wrist braces offer a conservative approach to managing CTS. They are risk-free and can be used as a first line of defence, delaying the need for more invasive treatments in many cases.
- Cost-Effective: Wrist braces are an affordable alternative to long-term medications, physical therapy, or surgery. Their one-time cost and reusability make them a practical option for budget-conscious individuals seeking relief.
- Ease of Incorporation: Braces are versatile and suitable for use during various activities. Whether working, engaging in leisure pursuits, or sleeping, they integrate seamlessly into your routine without significant disruption.
- Delays Progression: Consistent use of wrist braces can slow the progression of CTS by preventing further nerve compression. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who want to manage symptoms while exploring additional treatment options.
- Improves Sleep Quality: Nighttime splints prevent the involuntary wrist bending that often exacerbates CTS symptoms during sleep. By maintaining a neutral position, these braces reduce nighttime discomfort, allowing users to wake up feeling rested and pain-free.
Types of Wrist Braces
Different wrist braces cater to varying levels of CTS severity and individual needs. Understanding the options available can help users choose the most effective brace for their condition.
- Standard Wrist Braces: These provide general support and are suitable for managing mild to moderate symptoms. Their simple design offers stability while allowing limited wrist movement, making them ideal for everyday use.
- Night Splints: Explicitly designed for overnight use, these braces keep the wrist in a neutral position to prevent strain while sleeping. They are particularly effective for individuals experiencing worsening symptoms at night.
- Custom-Fitted Braces: Tailored to fit an individual’s wrist anatomy, these braces provide maximum comfort and support. They are often recommended for individuals with unique needs or those recovering from surgery.
- Compression Braces: These lightweight braces offer mild compression, which helps reduce swelling and improve circulation in the wrist and hand. They are a great option for managing early-stage symptoms or mild discomfort.
- Ergonomic Braces: Perfect for workplace use, ergonomic braces offer support while allowing a controlled range of motion. They help reduce strain during repetitive tasks like typing or using a mouse.
- Dual Function Braces: Combining immobilization and compression, these versatile braces provide stabilization and improved circulation benefits. They are ideal for individuals requiring comprehensive support for more severe symptoms.
Considerations When Choosing a Wrist Brace
Selecting the right wrist brace is essential for achieving effective relief and ensuring long-term comfort. Here are the key factors to keep in mind when making your choice:
- Fit and Comfort: A properly fitting brace should feel snug but not overly tight. Ill-fitting braces can restrict blood flow or cause discomfort, potentially worsening symptoms. Opt for a size that aligns with your wrist measurements.
- Material: Breathable, lightweight materials such as neoprene or mesh are ideal for long-term use. These materials prevent skin irritation and allow for better ventilation, keeping the wrist cool and comfortable throughout the day.
- Adjustability: Braces with adjustable straps provide a customized fit, ensuring maximum support and flexibility. Adjustable features also make it easier to adapt the brace for different activities or stages of recovery.
- Level of Support: Consider the severity of your CTS when selecting a brace. Mild symptoms may only require compression braces, while moderate to severe cases might benefit from immobilizing braces or custom-fitted options.
- Intended Use: Determine whether you’ll primarily use the brace during work, leisure activities, or sleep. Night splints, for example, are specifically designed for nighttime use, while ergonomic braces are better suited for work-related tasks.
- Durability: High-quality materials and robust construction ensure the brace can withstand frequent use without losing effectiveness. Durable braces are a cost-effective investment, especially for those requiring long-term support.
By carefully considering these factors, individuals can select a wrist brace that aligns with their specific needs, ensuring effective symptom management and improved quality of life.
Effectiveness of Wrist Braces
The effectiveness of wrist braces for managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition, consistency of use, and whether the braces are combined with other treatments. For many individuals, wrist braces provide significant relief by maintaining the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve, and preventing further irritation.
Factors Affecting Effectiveness
- Severity of CTS: Wrist braces are most effective for mild to moderate cases of CTS. They help prevent symptoms from worsening by reducing strain on the nerve. Braces may offer temporary relief for severe cases but typically need to be combined with advanced treatments like injections or surgery.
- Duration of Use: Consistent use of wrist braces, especially during repetitive wrist movements or sleep activities, can significantly alleviate symptoms. Intermittent use, on the other hand, may not yield sustained benefits.
- Combination Therapy: The effectiveness of wrist braces improves when used alongside other treatments. Combining braces with ergonomic adjustments, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes enhances symptom relief and supports long-term recovery.
- Proper Fit: Braces that fit snugly and align the wrist correctly are more effective in reducing nerve compression. An ill-fitting brace may exacerbate symptoms or fail to provide adequate support.
- Timing of Use: Wearing wrist braces during high-risk activities (e.g., typing, gardening, or using hand tools) or at night when symptoms worsen ensures better management of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
While wrist braces are not a cure, their consistent and proper use can significantly reduce pain, improve functionality, and slow the progression of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Additional Management Strategies
While wrist braces are critical in managing CTS, their benefits are maximized when combined with other strategies that address underlying causes and prevent symptom progression. Incorporating these approaches into your treatment plan can enhance relief and improve long-term outcomes:
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Optimizing your workstation to minimize wrist strain is crucial. Use ergonomic keyboards, mice, and wrist supports to maintain a neutral wrist position during activities. Adjust your chair and desk height to prevent awkward angles.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Regularly perform wrist stretches and strengthening exercises to improve flexibility and support the muscles surrounding the wrist. Exercises like wrist curls, finger stretches, and tendon glides can help alleviate tension.
- Physical Therapy: Consulting a physical therapist can provide targeted interventions, such as manual therapy or tailored exercise programs, to relieve CTS symptoms and improve wrist mobility.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing repetitive wrist movements, taking frequent breaks, and alternating tasks can prevent overuse and reduce strain on the wrist.
- Medications: Over-the-counter NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen can help manage inflammation and pain during flare-ups.
- Corticosteroid Injections: For moderate to severe cases, corticosteroid injections may provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation around the median nerve, especially when braces and other strategies fall short.
Combining these strategies with wrist braces creates a comprehensive approach to managing CTS, ensuring symptom relief and preventing further complications.
Read More: Uncovering the Potential of Modern Wrist Braces to Improve Wrist Stability
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If symptoms persist or worsen despite consistent use of wrist braces and other management strategies, seeking professional medical advice is essential. Persistent numbness, tingling, or weakness may indicate severe nerve compression requiring advanced interventions.
What to Expect During a Consultation
- Electrodiagnostic Tests: Tests like nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) are performed to assess the severity of nerve compression and identify any nerve damage.
- Corticosteroid Injections: If inflammation is significant, your healthcare provider may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce swelling and pressure on the nerve, providing temporary relief.
- Surgical Intervention: For advanced Carpal Tunnel Syndrome that doesn’t respond to conservative treatments, carpal tunnel release surgery may be necessary. This minimally invasive procedure involves cutting the ligament pressing on the median nerve to relieve pressure and improve symptoms.
Consulting a healthcare professional ensures you receive an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan to manage your condition effectively. Early intervention can prevent permanent nerve damage and restore wrist functionality.
Conclusion
Wrist braces are a valuable tool in managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, offering symptom relief and supporting the healing process. However, their effectiveness can vary, and they are often most beneficial when used with other treatment modalities. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to individual needs.